Today I want to continue our discussion on insurance and specifically talk about health insurance. We’re talking about why to have it, the two primary plans that are available, three or four different numbers to focus on when selecting a plan, and the best places to get it.
Now, I don’t know if this or not, but medical insurance and healthcare is expensive. In fact, these expenses equate to the number one cause of personal bankruptcy. Research after research, report after report, continually show that this is the primary cause of all personal bankruptcies. Almost two out of three.
And that’s what I want to help protect you against in this episode. But first a story.
Example of Why You Must be Insured
So, this is some people that I know personally they might listen to this. So, I won’t use their real names. We’ll call them John and Carol. John and Carol got married in their mid-twenties or so. And after a couple of years of being married, they were elated that they were found out that they were having a baby.
And all throughout the pregnancy, everything kind of looked normal. Towards the end, there was a couple of instances where things didn’t look exactly right. They got some clues that maybe things weren’t happening right from a developmental perspective, but they didn’t. Exactly. No, it was going on.
Well, Carol went into labor at their local hospital and, everything seemed pretty good. But right after the child was born, they immediately recognize that there was some major. Problems, developmental problems with their child. And so, they basically were transported to a major city where they could get some more care.
And to make a long story short, that little baby spent, two to three months in the NICU had somewhere between, five to 10 to 15 different surgeries to repair all kinds of things. And that child has, and still does to this day, a lot of developmental. Issues that, it wasn’t anybody’s fault.
It just, kind of how God made that girl and has blessed them with a special opportunity., the reality is that God only gives special people children with disabilities because it takes a special parent to raise a special child like that. And so, they were their kind of staying at the Ronald McDonald house.
Great opportunity for them to stay there. And while their child was getting all this care they needed. But there’s a cost associated with those things. And, I don’t know the exact number, but I imagine if they would have added up all the bills of all the costs of all the surgeries, all the doctors and the staff and the nurses and the medicines and all this stuff, it probably would have been over a million dollars. But because Carol was employed through a good employer that had good medical insurance, they walked out with simply a 250 copay and all the rest was paid for by insurance. If they didn’t have insurance, they weren’t properly insured. They would have filed bankruptcy. And oh, when you file bankruptcy, it’s not like you just get the file bankruptcy on the debt and keep all the other money you have.
No, they take all the money you have minus couple of things to pay that debt down, and then you file bankruptcy on the rest, which is why we have insurance. As one of the two primary rails protect you and your wealth in the financial framework.
Two Types of Plans
Now, when it comes to healthcare insurance plans, there’s generally two types of an HMO and a PPO. So, an HMO is a. Health maintenance organizations type of healthcare plan where members are provided insurance through a network of doctors and hospitals and other providers that all really work together.
Generally, you’ll have a primary care physician. It’s kind of the gatekeeper. This is your main focal point. And anytime you need specialized care, if you need to go cardiologist or whatever it might be, you go to your primary care doctor first and they give you a referral. To that specialized physician the advantages are that the premiums are lower, and you have centralized healthcare.
That primary physician is kind of keeping track of everything. So, everything’s, in your records, centralized in the system, things like that. The disadvantages though of an HMO is that if you need specialized care, you need to go to your primary doctor. So again, it kind of acts like a gatekeeper and so you can’t just go to anybody you want to see because you must go to an in-network provider.
So, there’s a group of people that work together and you must see them. You don’t have a lot of flexibility to go see any doctor you choose, which leads us to. The PPO, the PPO is a preferred provider organization. Again, it’s a type of medical plan that provides participants access to healthcare providers, hospitals, physicians through a network.
And this network isn’t, through a centralized organization. It’s really done through contracts and insurance has a contract with this provider insurance as a contract with this hospital and so on and so forth, but there’s a lot more flexibility. And so now one of the advantages are you don’t have a primary care physician.
You can go see any doctor you want, as long as they’re in network. So, you have a lot more flexibility. And you don’t need a referral to go just see if you need to go see a cardiologist, you can just one day get up and go make an appointment with a cardiologist. You don’t have to go through and get a referral.
So, it gives you a lot more flexibility. But there’s some downsides with that. That flexibility comes generally with more costs. So, the premiums cost more. Little bit higher out of pocket plans. And you then become that central focal point of keeping track of all your records because the cardiologist that needs to talk to the obstetrician or the OB or, whoever else they don’t talk.
And so, you must take the records from one to the other and help them. This doctor asked me on this medicine that you need to keep track of that. So, it does become a little bit more taxing on you. So again, that with that flexibility comes more responsibility and more costs, but it’s a trade off as to what you personally desire.
Now when it comes to selecting a plan, there’s really three or four different numbers that you want to focus on or explore.
Numbers to Focus On
Those are the premiums, the deductible, the coinsurance amounts, and the maximum out of pocket costs. So, let’s unpack those and then I’ll show you an example of where to find them. So, number one is the premiums. The premiums are what you pay. Each month, regardless of use any of the services or not, that’s what you pay.
And that’s mostly the number that people are aware of and that they focus on. If you get a high deductible plan, which generally is a deductible more than 1, 500 as a single person or 3000 as a family member, you could have a plan that also has then a Health savings account associated with it.
And even if it there’s one not associated with that, you individually could open a health savings account and deduct it on your taxes. So, the way a health savings account works is you save money pretax you could invest it into, mutual funds, things like that. And then you can use that.
Proceeds for future medical expenses without ever being taxed on it. An HSA is sort of like a Roth IRA, but for medical expenses. So, great thing that’s kind of come to light the last decade or so, become more and more popular, very popular. Generally, two types of people that use it. Ones that would never go to the doctor.
Or number two, those that go to the doctor all the time, those are the two types of people that would be, it’s in the middle of where you kind of got some issues there. So, premiums are what you pay each month. The deductible, the deductible is the amount of money that you pay out of pocket first before the insurance covers any expenses.
So, these have an indirect relationship between the deductible and the premium. So, the higher, the deductible. All right. The more you’re going to pay, the more your risk you’re retaining, and therefore the lower the premiums, the lower the deductible, the more risk you’re transferring to the insurance provider, they’re going to pay out sooner, so therefore the higher premium.
So, there’s an indirect relationship between premiums and deductible. So again, the deductible is where, you have a good solid emergency fund, or at least a thousand-dollar emergency fund, from a baby step perspective, you then can. Take some more risks on that deductible. So, some of these things with finances start to get intertwined here.
The co-insurance is the split amount that after the deductibles meet of a percentage that you will pay, and a percentage of the insurance company will pay. So generally, this is., 90, 10. So the insurance company would pay 90%. You pay 10, could be 80, 20. The insurance company would pay 80 percent of the cost.
You pay 20, 70, 30. And I think the lowest is 60 40. I think it’s about the lowest they go to these days. So that’s where, the co-insurance comes in, they split pay. And then the, the fourth number that you want to pay attention to. is that of the maximum out of pocket cost. The maximum out of pocket cost is the maximum amount you would pay between your deductible and your coinsurance for any given year.
Once you hit that amount, that out-of-pocket cost, the insurance will pay 100 percent of all expenses thereafter. So, if you have a lot of medical expenses in one year, this is a number what would be the maximum out of pocket you would pay. So again, this is where you want to have a good solid emergency fund.
That’s that amount or higher so that if you had a major medical expense and an incident each year, you have the maximum out of pocket costs and that the insurance will pay the rest. Now, there’s obviously some special limitations with different things like having a baby emergency room visit and co pays and things like that.
But for the most part, those are kind of minor things. We want health insurance to protect against the major expenses, the things that will. Potentially bankrupt you.
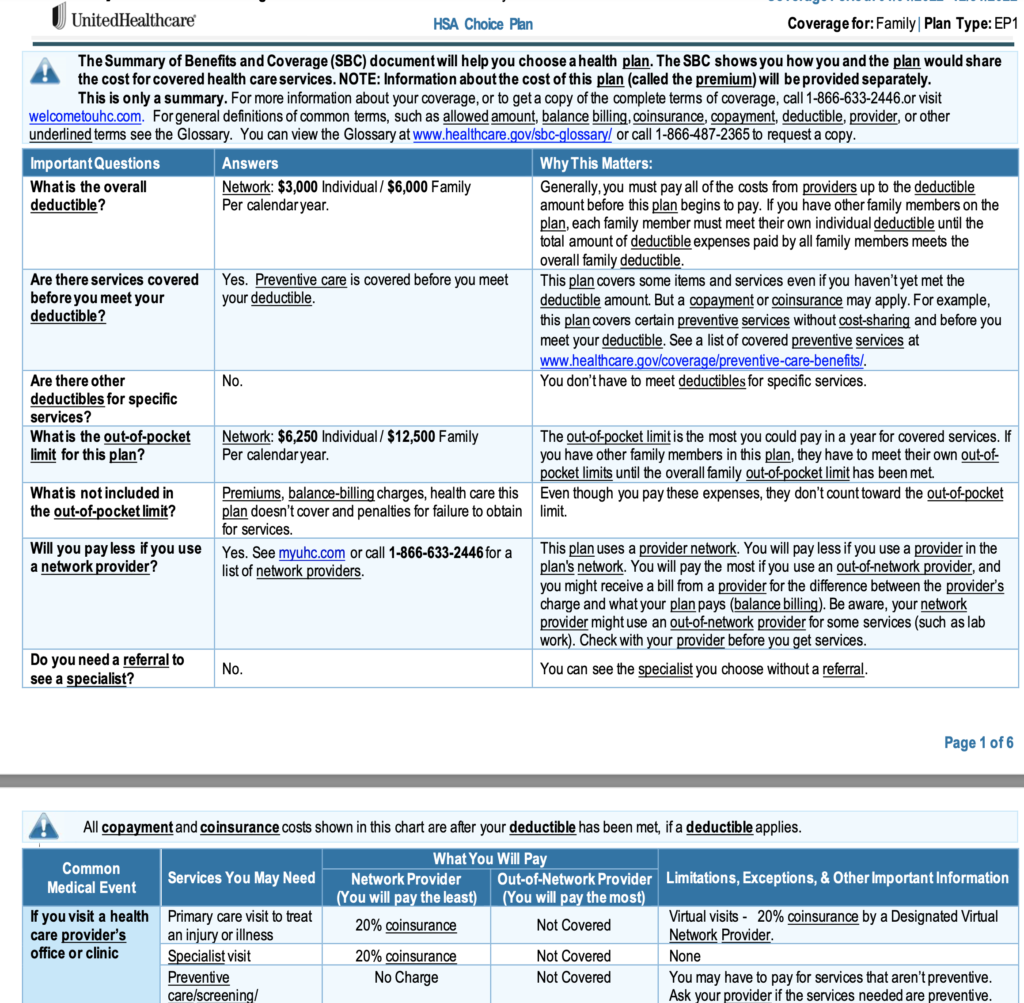
Now, one of the things that the government has done to help you identify those numbers is it has provided a standardized means for insurance companies to provide a summary of benefits and coverage. This is an example here that I have from a client of mine from a couple years ago. And so, we can see these numbers and identify them very easy.
So, number one is what’s their deductible. So here is their deductible 3, 000 per person, 6, 000 per family. So, if you’re a single person you would pay the first 3, 000. If your family husband and wife, you would pay 6, 000, but if you each have expenses with, and you have two or three kids, the maximum for the family would be 6, 000.
So that’s that number. The second is that of co-insurance. So, on the next page we can see for all the various services, the co-insurance. So, this is an 80 20, meaning that the insurance company would provide 80 percent of the coverage and they would pay 20 percent after that deductible was met.
The third number is that of the maximum out of pocket expenses. So again, for a family, it’d be 60 to 50 in this example, or 12, 500. So, if this family, you know, found me of Three or four or five were to have some major medical expenses where they all had hundreds of thousands or maybe millions of dollars of expenses.
The most they would pay is 12, 500. And so, the insurance company would cover everything above that. So, you can see by looking at this form here you can quickly identify those numbers very easily.
Where to Buy Insurance
So lastly, I want to talk about where to purchase insurance, right? So, there’s really three different places you can get insurance these days. Number one is through group plans, through your employers, right? That’s where most people get their health insurance. They have an employer.
Those employers have a group plan that they offer. In some case, they subsidize the premiums and pay a portion of for it. To help attract and retain you as a good employee at your employer. And so that’s the best place most people get their insurance for those that are retired. They have some other options that those are working might not.
So, for example, some employers have retiree. group plans that you can get insurance through them, or they would subsidize it. They would give you money as a credit to pay premiums. If you get it other places, those that retire from the military have the means to get TRICARE through TRICARE for life, right? So, a group plan through retirees that the military offers.
And if you’re retired and 65 years and older, you can get it through Medicare.
In the future, we’ll do a whole episode on Medicare. Cause it’s a unique system all to its own. The last place that if you can’t get through your group employer and you are not retired, and you don’t have means to get it through previous employers and the military Medicare is that of. The exchanges.
So, one of the affordable care act provisions that came out from 2009 10 was that of healthcare. gov. So healthcare. gov is a centralized place where you can get an individual policy in your state. And so, it really afforded the opportunity for people who didn’t have options through employers or through retired benefits, things like that to get insurance.
MicroAction
And so, here’s your micro action for the week. Try to find your healthcare. Sheet that summarizes sheet and see and identify the numbers that you have. What is your deductible? What is your coinsurance and what is your maximum out of pocket? My guess is you’re probably already familiar with the premiums that you pay.
The real takeaway from this is that you must have medical. insurance. It’s a no brainer. You must have it. You don’t want to put yourself in the position where you’re opening yourself up to bankruptcies. Two out of three of those bankruptcies that are filed each year because of medical insurance.
And in some cases, a lot of cases, maybe they could have been prevented. So, in this episode, we talked about why to have medical insurance. We talked about the two primary types of plans. We talked about the four numbers to focus on when you’re selecting a plan. and the best place to get a plan. So, I hope this helps you in your financial journey.
If you have any questions or comments, you can leave them on below or send an email to Mike at true health dot show. And I’ll try to do my best to respond. And until next time, I hope you have a great day.


